-
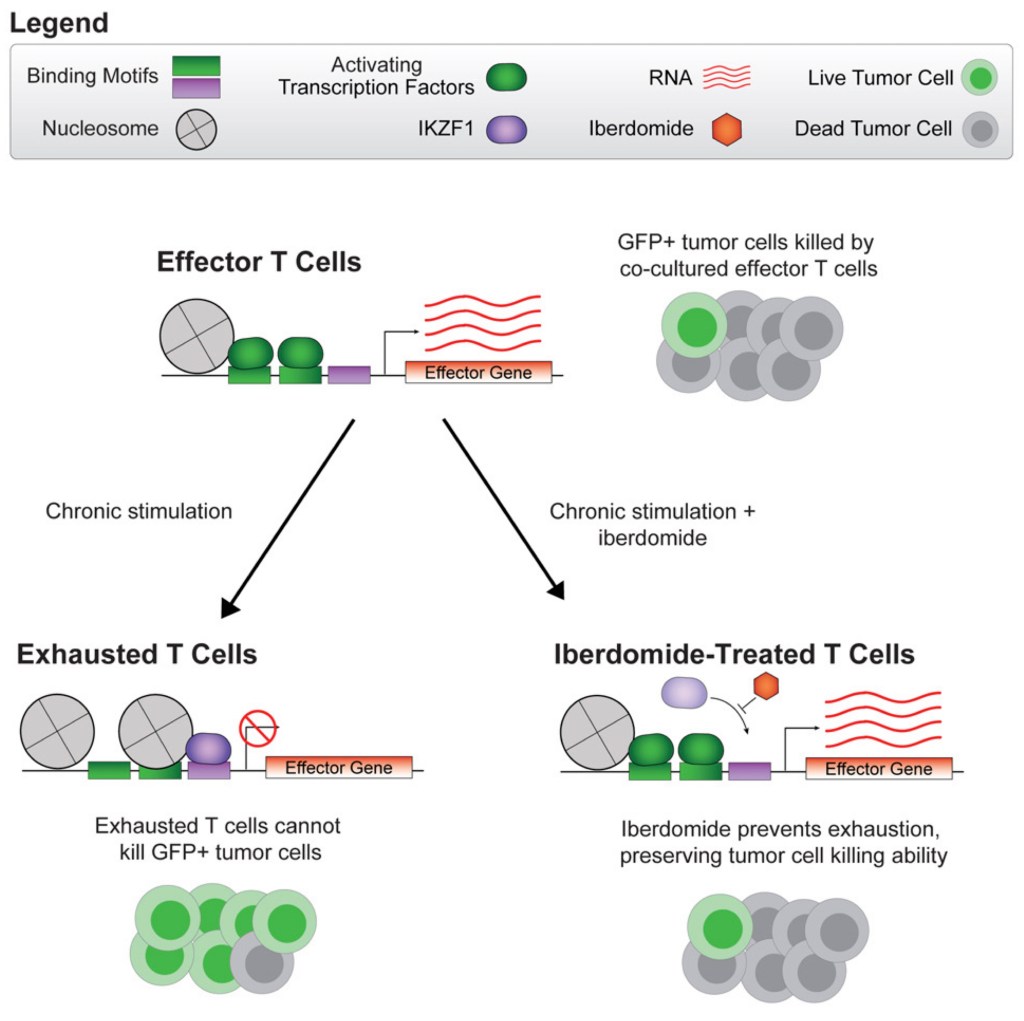
Reversing T Cell Exhaustion: A New Role for IKZF1 Degradation
Read more: Reversing T Cell Exhaustion: A New Role for IKZF1 DegradationIn a recent publication in Cell Report Medicine (November 19, 2024), the authors explore a novel strategy to prevent T-cell exhaustion in the context of immuno-oncology. While adoptive cell therapies involving in vitro modified T cells can avoid immune exhaustion, the uncontrolled proliferation of these modified cells may lead to severe side effects, including potential…
-
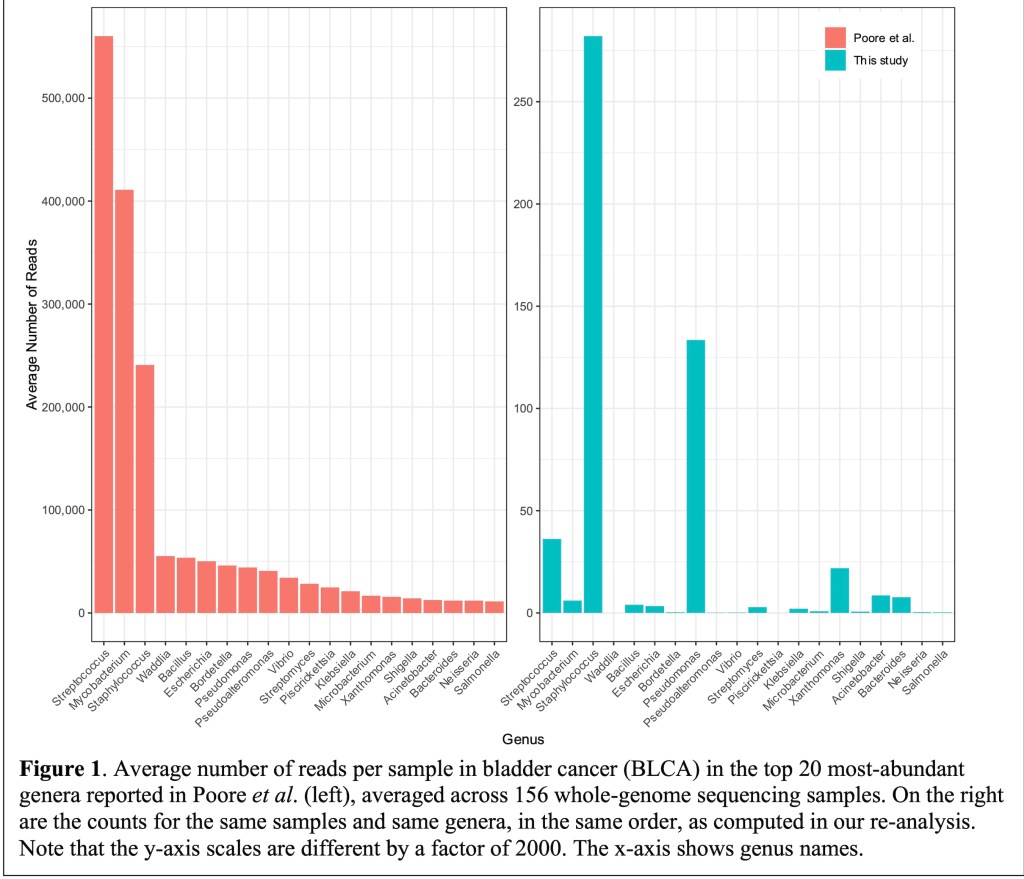
Standard methods may produce (published) nonsense
Read more: Standard methods may produce (published) nonsenseStandard methods sometimes produce nonsense. In 2020, researchers of UC La Jolla published in Nature their discovery that microbiome present in cancer samples identifies their cancer identity and type, using authoritative TCGA data base, hg19 genome assembly and Kraken pipeline to identify microbial reads in TCGA samples. Currently, a group of (mostly) Johns Hopkins researchers…
-
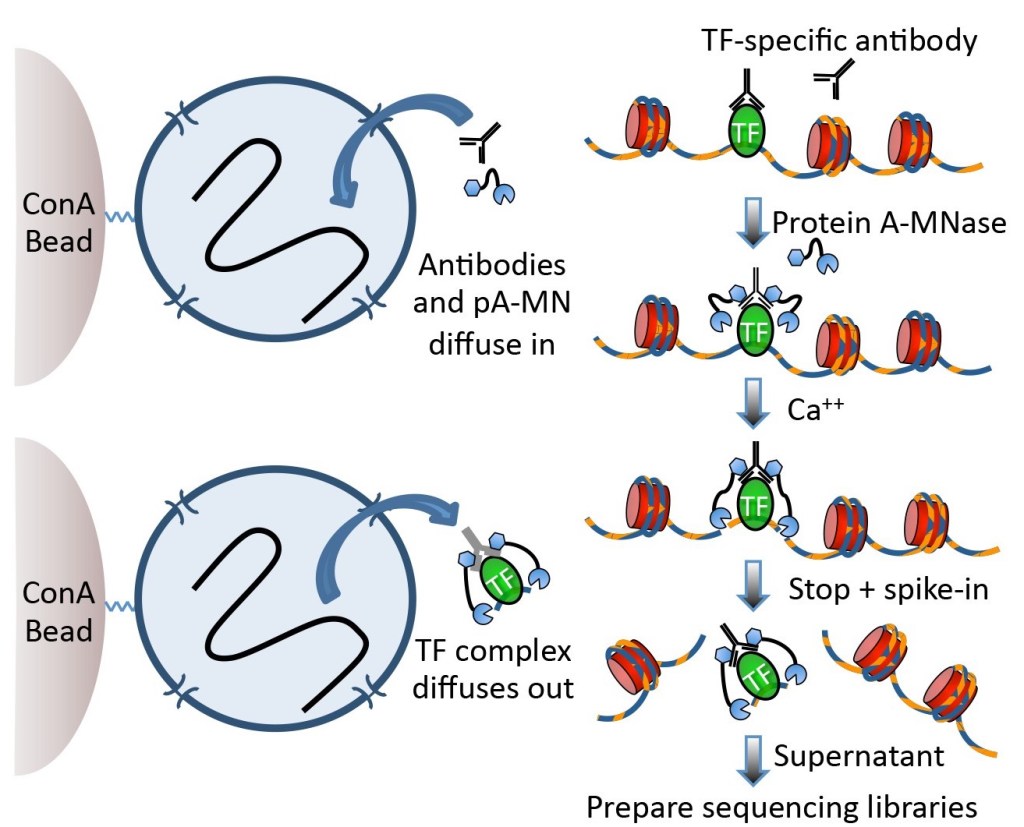
CUT&RUN
Read more: CUT&RUNRecent papers on chromatin modification in cells increasingly use CUT&RUN of Skene and Henikoff, 2017. DNA cutting enzymes combined with an antibody enter cell nucleus and cut DNA fragments at sites where antibody binds to antigen, producing short fragments only at antigen binding sites. These short fragments exit nucleus and are collected. This yields very…
-
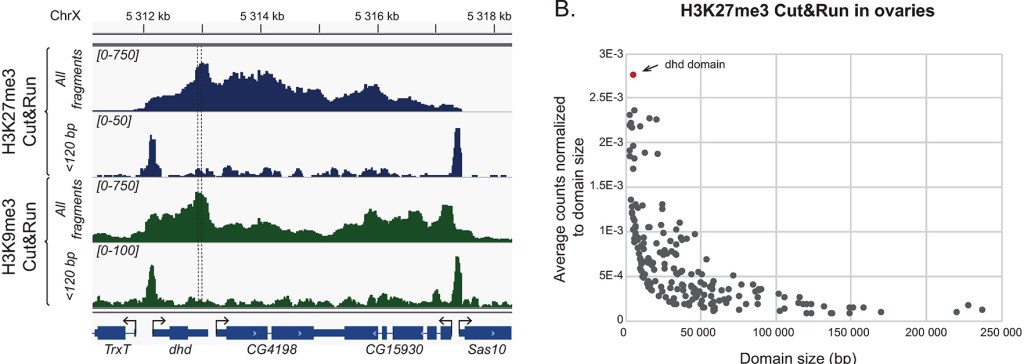
Improved mapping in heterochromatin and fruit fly
Read more: Improved mapping in heterochromatin and fruit flyWhile Skene and Henikoff described this benefit of CUT&RUN, it is not easy to find a publication that takes advantage of that. But Torres-Campana et al. use it in a great paper in PLOS Genetics, 2022. A key gene in fruit fly reproduction, DHD (deadhead), is included in a very small heterochromatin domain and at…
